A transparent micro OLED display is a type of screen that can show images while letting light pass through it. This means you can see digital content on the screen without blocking what is behind it. It is smaller and more advanced than regular transparent OLED displays. These displays are used in devices like AR glasses, heads-up displays, and smart devices.
This article will explain how a transparent micro OLED display works, its structure, applications, and key benefits.
How Does a Transparent Micro OLED Display Work?
A transparent micro OLED display works by creating light from tiny organic layers called OLEDs. Each pixel produces its own light, so no backlight is needed. This makes the display bright and clear.
The transparency is possible because some layers in the display let light pass through. When the pixels are off, you can see through the display like glass. When pixels are on, they show images or data.
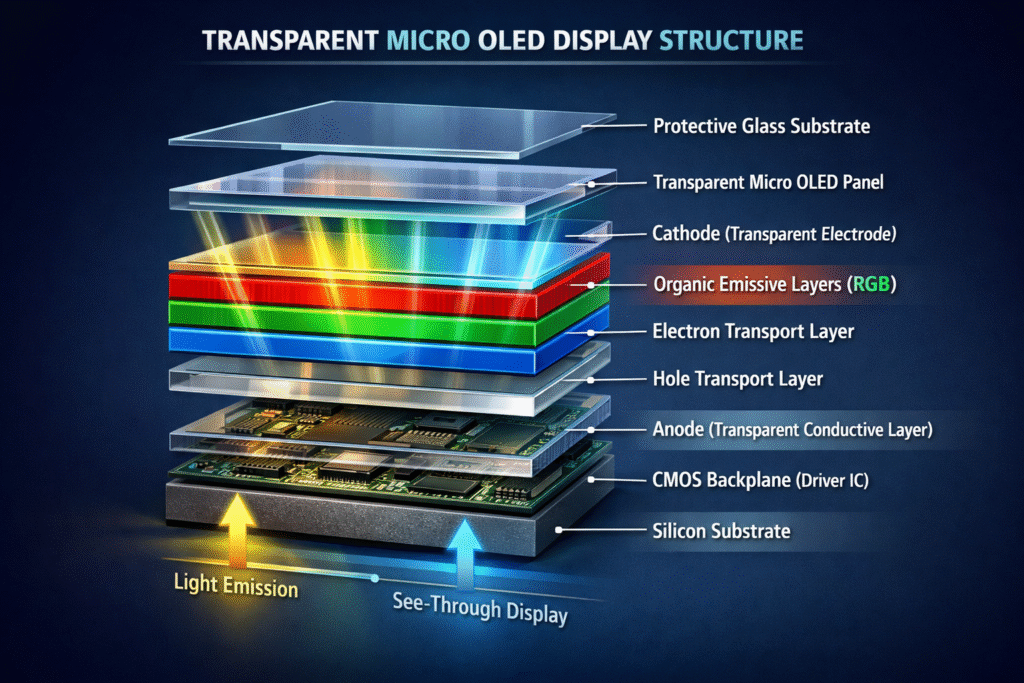
Structure of a Transparent Micro OLED Display
1. Protective Glass Substrate
A clear glass layer that protects the delicate OLED layers from scratches, dust, and damage. It keeps the display safe while letting light pass through.
2. Transparent Micro OLED Panel
The main display layer made of tiny OLED pixels. It creates bright, colorful images while remaining see-through when pixels are off.
3. Cathode (Transparent Electrode)
A thin transparent layer that sends electrons to the OLED layer. It helps the pixels light up without blocking the view.
4. Organic Emissive Layers (RGB)
Tiny layers of organic materials that produce red, green, and blue light. These layers are what actually create the colors you see on the display.
5. Electron Transport Layer
A layer that moves electrons from the cathode to the organic emissive layer, making the pixels work efficiently.
6. Hole Transport Layer
This layer moves positive charges (holes) from the anode to the organic layers. It balances the electrons so the light is stable and bright.
7. Anode (Transparent Conductive Layer)
A clear conductive layer that sends positive charges to the OLED. It is transparent so it does not block the image or background.
8. CMOS Backplane (Driver IC)
A tiny electronic circuit layer that controls each pixel. It decides which pixels turn on, off, or change color.
9. Silicon Substrate
The base layer that supports the whole display and holds the backplane. It gives structure and stability to the display assembly.
Key Differences Between Transparent OLED and Transparent Micro OLED
-
Size of Pixels: Micro OLEDs have smaller pixels, making images sharper.
-
Resolution: Transparent micro OLED displays can show higher resolution compared to standard transparent OLEDs.
-
Applications: Micro OLEDs are used in devices like AR glasses and VR devices, while standard transparent OLEDs are mainly for larger screens.
-
Power Consumption: Micro OLEDs use less power because they do not need a backlight.
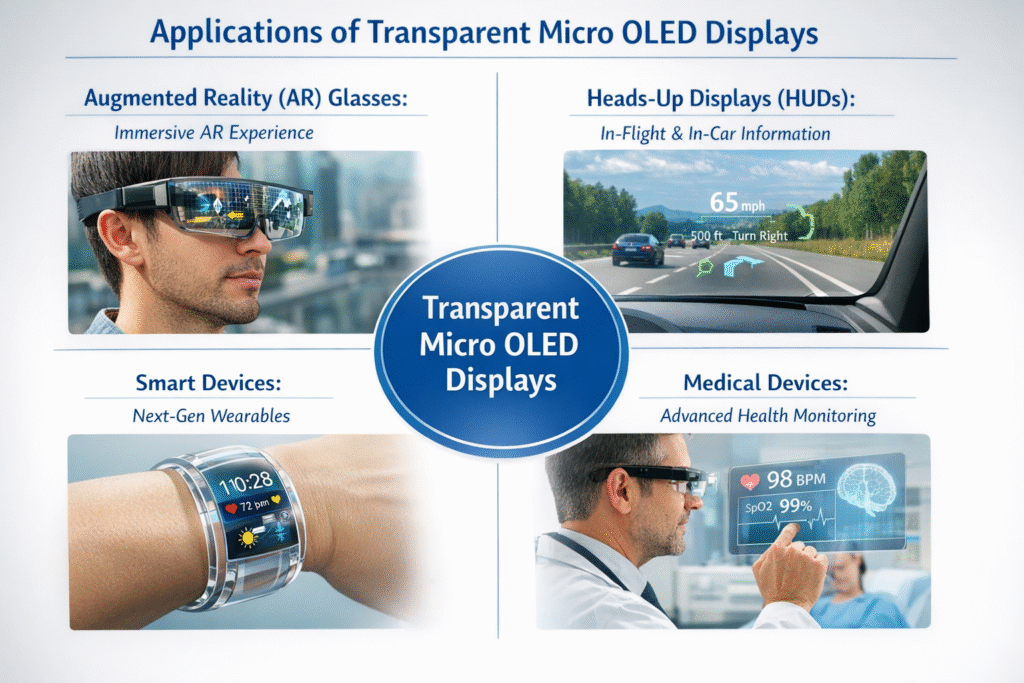
Applications of Transparent Micro OLED Displays
Transparent micro OLED displays are used in several areas:
-
Augmented Reality (AR) Glasses: Shows digital images while you see the real world.
-
Heads-Up Displays (HUDs): Displays information on car windshields without blocking vision.
-
Smart Devices: Smart glasses, wearable devices, and small transparent screens.
-
Medical Devices: Some advanced medical tools use them for real-time imaging.
Challenges in Manufacturing Transparent Micro OLED Displays
Making transparent micro OLED displays is difficult:
-
Tiny Pixels: Manufacturing very small pixels requires precision.
-
Layer Alignment: Each layer must be perfectly aligned to maintain transparency and display quality.
-
Cost: Production is expensive because of complex equipment and materials.
-
Durability: Maintaining transparency without damaging OLED layers is challenging.
User Experience Benefits Compared to Other Technologies
Transparent micro OLED displays offer several advantages:
-
Better Visibility: Users can see both digital content and the real world.
-
High Image Quality: Bright colors and high contrast.
-
Energy Efficient: Does not need extra backlight, saving battery.
-
Compact Design: Can fit into small wearable devices easily.
Environmental and Durability Considerations
-
Durability: Micro OLED layers can be sensitive to water and dust, so devices often need protection.
-
Energy Use: They are more energy-efficient than LCDs, which is better for the environment.
-
Longevity: With proper design, these displays can last several years without losing transparency or brightness.
Conclusion
A transparent micro OLED display is a compact, advanced screen that delivers high-quality images while remaining see-through. Its tiny OLED pixels, precise layered structure, and energy efficiency make it ideal for AR glasses, heads-up displays, and wearable devices.
Even though manufacturing and durability can be challenging, the clear visuals, low power use, and enhanced user experience make transparent micro OLED displays a key technology in modern optoelectronics.
At ARVR Optical, we provide a wide range of optical components, display modules, and electronic solutions in bulk to support your projects. Contact us today to get high-quality products and services for your business needs.
FAQs About Transparent Micro OLED Displays
Q1: Can you see clearly through a transparent micro OLED display?
Yes, when the pixels are off, the display is nearly like clear glass.
Q2: Are transparent micro OLED displays expensive?
Yes, they are more costly than standard screens because of the small pixels and precise manufacturing.
Q3: What devices use transparent micro OLED displays?
They are mainly used in AR glasses, car HUDs, medical devices, and smart wearables.
Q4: Do they consume more power than regular OLEDs?
No, micro OLEDs are more energy-efficient because each pixel produces its own light.